From the crudest low-effort phishing attempts to the most sophisticated high-tech hacks, the hits never stop coming. An effective defense against these threats requires a consistent and comprehensive security posture like the one outlined in the ISO 27001 standard.
As daunting as these threats seem, up to 80% can be stopped by adopting security controls. By implementing ISO 27001, you can help protect your organization from modern cyberattacks, establish a high level of resiliency, and maintain a safe and trustworthy reputation.
The last major update, in 2022, introduced eleven new controls designed to keep businesses and their data safer. Let’s examine what these controls involve and why they’re essential for information security management systems.
ISO 27001: What is it, and why is it so important?
ISO 27001 represents the international benchmark for managing information security systems. It was created in 2005 by the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission. ISO 27001 defines the essential requirements for any organization that takes a systematized approach to data protection and cybersecurity.
When an organization is ISO 27001 certified, it proves they’re following best practices for managing their technology, policies, and human resources to optimize security. Given the prevalence of cyberattacks directed at every online organization, from small businesses to massive enterprises, a comprehensive and standardized approach ensures that risk is managed appropriately and that there is an ongoing process to identify and address vulnerabilities.
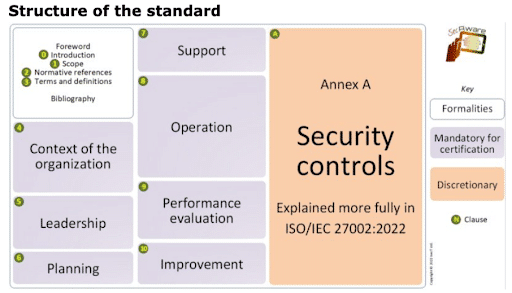
What are ISO 27001 controls?
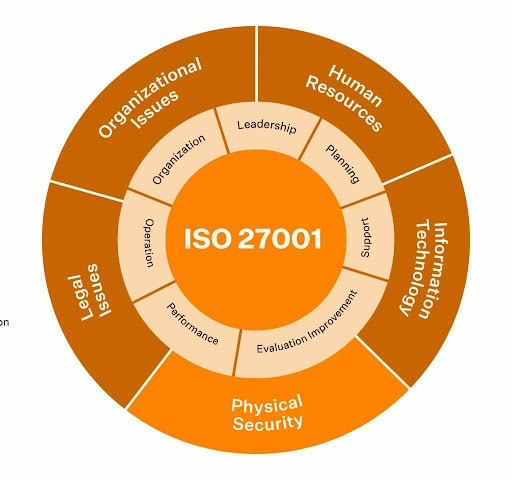
ISO 27001 provides guidelines for leadership, planning, support, operational implementation, performance evaluation, and continual improvement, but the most detailed requirements of the standard are the controls listed in a section called Annex A. The standard originally contained 114 different controls organized into fourteen domains, covering fourteen critical areas of information security.
ISO 27001 – Annex A
- Information security policies
- Organization of information security
- Human resource security
- Asset management
- Access control
- Cryptography
- Physical and environmental security
- Operations security
- Communications security
- System acquisition, development, and maintenance
- Supplier relationships
- Information security incident management
- Information security aspects of business continuity management
- Compliance
Each control provides direction for organizations on how to identify threats, reduce their exposure, and take the right actions in response.
However, not every organization needs to adopt all of the controls. They can be applied as needed, as determined by a comprehensive risk assessment process. A related standard, ISO 27002, provides information about implementing these controls.
What are the benefits of adopting ISO 27001 controls?
By identifying the controls relevant to their operations and implementing them, organizations can build a comprehensive, optimized system for detecting and managing cyber threats. This confers several direct benefits.
Most importantly, it protects your digital infrastructure and reduces the likelihood of significant data losses from a breach or ransomware incident. It also ensures that you’ll comply with many of the data protection requirements mandated by government and industry regulators.
Being able to highlight your security controls and ISO 27001 certification also demonstrates your commitment to strong cybersecurity practices—and their continual improvement—to customers, business partners, and other stakeholders, helping you maintain a positive reputation.
Finally, even in the unfortunate event that a cyberattack does impact your organization, ISO 27001 controls can mitigate the damage and get you back to normal operations as quickly as possible.
What has changed in ISO 27001?
The ISO 27001 standard received its last major update in October 2022. In the nine years since the previous revision, online fraud and cybercrime methods have undergone considerable evolution. The changes introduced in 2022 have improved the standard’s capability to deal with the threats organizations are currently facing.
Many of the changes were relatively minor, having to do with restructuring or adding to various clauses:
- The Internal Audit clause was divided into two sub-clauses.
- The Management Review clause was divided into three sub-clauses, with a new mandatory item added.
- A new clause (6.3: Planning for Changes) was added.
The most significant changes, however, have to do with the Annex A controls. The control structure was revised, the fourteen domains were grouped into four categories, some of the original 114 controls were merged together, and eleven new controls were added, bringing the new total to 93.
What are the 11 new ISO 27001 controls?
If an assessment of your organization determines that you have the relevant risk factors, these controls can provide concrete steps toward safeguarding yourself.
1) 5.7: Threat Intelligence
Gather data related to information security threats, analyze it, and generate intelligence that you can use to inform preventative and responsive actions. Successful implementation of this and other controls depends on organizational staff being able to recognize threats and respond appropriately. Training platforms like CybeReady can be one of the best ways to educate staff on their roles in optimizing the efficacy of ISO 27001 controls.
2) 5.23: Information Security for Use of Cloud Services
Establish secure processes for using, terminating, and managing cloud services. Because cloud data is not under the direct physical control of the organization, strong policies and user training are critical for ensuring data integrity.
3) 5.30: Information and Communications Technology Readiness for Business Continuity
Maintain secure and reliable ICT systems to maintain communications and functionality in the event of a disruptive cyberattack. Ensure you have adequate planning, hardware, and training to ensure continuity. Procedures should be implemented to verify data integrity after a breach has occurred.
4) 7.4: Physical Security Monitoring
Monitor and secure areas where sensitive data and critical hardware are stored to prevent unauthorized access. While many cyberattacks are carried out entirely online, improperly secured servers, devices, and network components may be targeted in person. Advisable measures may include cameras, alarm systems, and security patrols.
5) 8.9: Configuration Management
Define appropriate security configurations for your technological assets and monitor them regularly to prevent unauthorized changes and configuration drift. Configuration setup and review processes must be thoroughly documented.
6) 8.10: Information Deletion
Establish data retention policies and delete stored data when it is no longer needed. Work to minimize the storage of sensitive data not being used for business purposes. Users should receive training on when and how to safely delete unneeded records.
7) 8.11: Data Masking
Whenever possible (such as during development or testing), utilize data masking procedures such as encryption or anonymization to obfuscate personal information and other sensitive data. Educate staff about the proper circumstances and procedures for data masking.
8) 8.12: Data Leakage Protection
Take appropriate steps to minimize leakage when data is stored, transferred, or processed. Monitor channels where leakage could occur, such as network components, mobile devices, and removable storage. Create policies and processes that minimize the risk of leakage and train users on best practices for securely handling data on the channels they access.

9) 8.16: Monitoring Activities
Continuously monitor your network, technological assets, and software applications for suspicious behavior. Inform users about which systems and activities will be monitored. When abnormalities are detected, take immediate and appropriate actions to determine if a security breach has occurred.
10) 8.23: Web Filtering
Limit access to external websites to prevent the spread of malware and discourage unsafe user behavior. Communicate policies and expectations to users and train them to recognize potentially dangerous sites that aren’t interdicted by the filter.
11) 8.28: Secure Coding
Establish secure coding principles to be followed by internal software developers. Maintain a secure development environment, implement measures to prevent unauthorized alterations to source code, document changes thoroughly, and provide applicable training to coders.
ISO 27001: Most Effective When Everyone Is On Board
Adopting ISO 27001 controls or preparing for a certification audit necessitates comprehensive education and training across the organization, which is essential for successful implementation. The effectiveness of these safeguards relies heavily on human intelligence. Often, catastrophic data breaches occur because perpetrators exploit users who fail to adhere to cybersecurity best practices.
CybeReady’s platform makes essential cybersecurity awareness training fast, engaging, and memorable for every stakeholder who has a role to play in upholding these standards and protecting your organization’s sensitive data.
Book a demo today to discover how easy it is to launch a training program to prepare your team to take on today’s most challenging cyber threats.

